Decision Tree with Bayesian Inference
Bayesian Inference is a mathematical method of updating beliefs (or probability) of any uncertainty based on evidence or observation from experimentation, using Baye's theorem. In Decision Tree Software, you can Update your belief/probability of Chance node events using Bayesian Inference. A tool for Bayesian Inference is built in for you.
Let's show a worked-out example. Say, you received a job offer and you are in a dilemma if you should take the job or wait for a better offer. The current job offer will pay you 80,000$/year but you think there is a 70% probability that if you wait, you may get a better offer. Should you wait or take the current offer at hand. The dilemma is shown in the following decision tree:
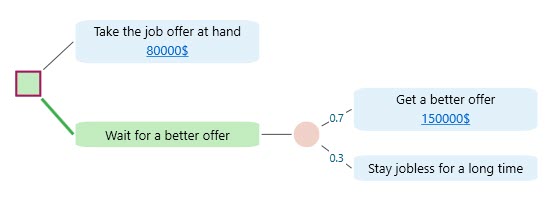
From the Sensitivity Analysis, you understood that the most sensitive variable in this decision tree is the probability of getting a better offer.
So, now you want to do some experiments and update the belief. You can upload your resume to an online job-finding website (like Monster.com, jobs.com, etc) and apply to various jobs and observe the rate of responses. If you get a good response, you can update your belief of the probability that you will get a better offer would be higher. But if you get very few responses, then your confidence in getting a better offer will be lower.
Let's start by selecting the Chance node and clicking the "Experiment" button from the flyover menu as shown below.
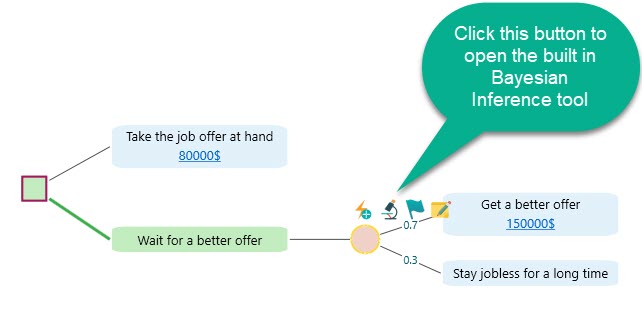
Once you click the experiment button, you will see the Bayesian inference tool like this:
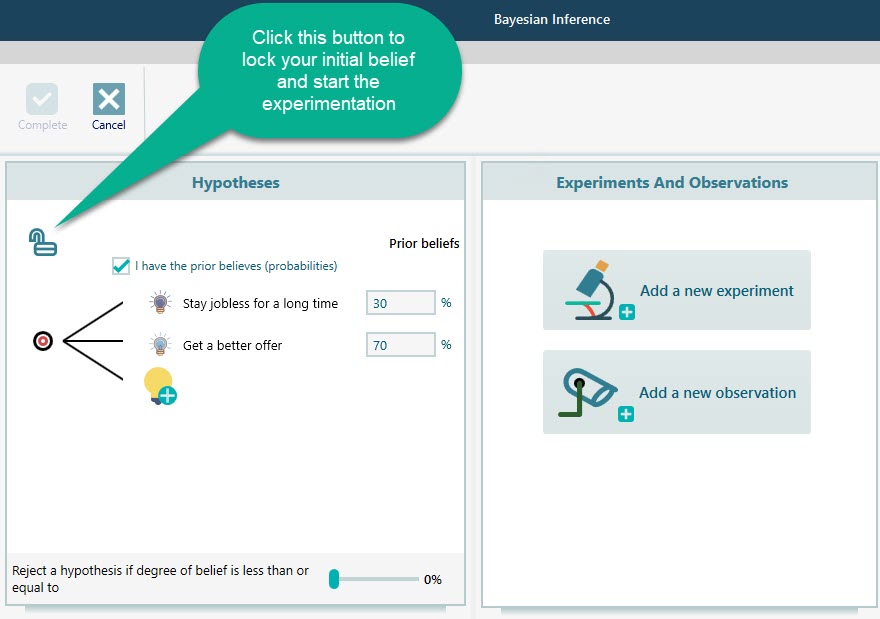
Once you click the Lock button to lock your initial beliefs, start experimentation by clicking the button "Add a new experiment".

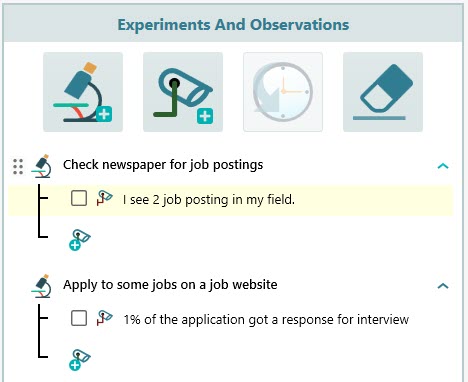
Then edit the experiment as "Check newspaper for job postings".

Add another experiment as "Apply to some jobs on a job website".

Now, check the newspaper and count the number of job postings in your field of interest. Once you get that information, add that information as an observation under the experiment "Check newspaper for job postings"
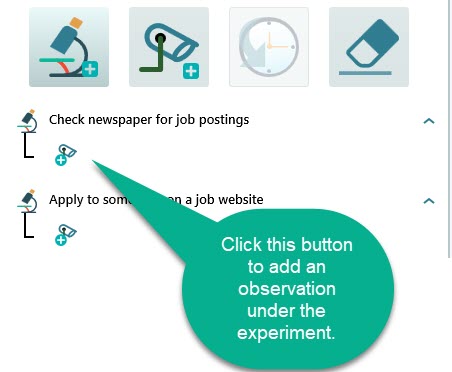
Update the observations for the experiments once you perform the experiments.
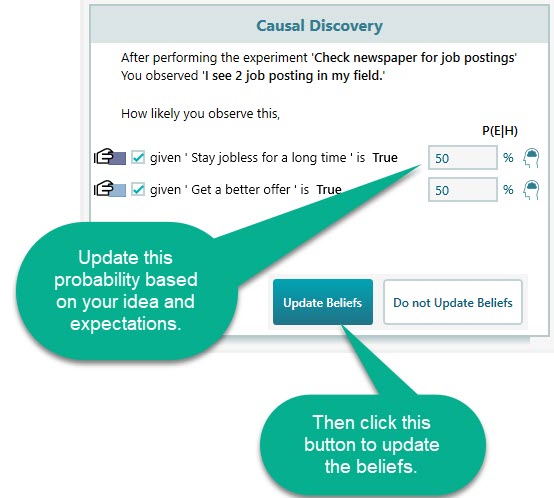
Now, it is time to perform a Causal discovery. Causal discovery is a methodology to find a cause based on observation. And here, the software uses Baye's theorem to update the beliefs.
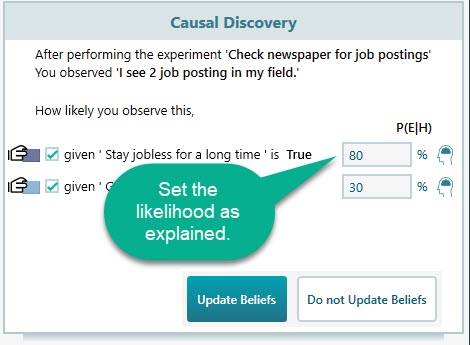
Now is the time to apply your reasoning skill. What do you think that you will stay jobless when you see 2 job postings? Did you expect more job postings? Then lower the likelihood number for observation "given 'Stay jobless for a long time is true. If you expected fewer job postings, then increase this number. Say, for example, you expected more job postings in the newspaper than 2, so, let's set the likelihood to 80%. Same way, set the likelihood of the observation "given 'Get a better offer' is True = 30%.
Once you click the Update Belief button, you will be asked a similar question for other experiments. Finally, you will see that your beliefs are updated as shown below.
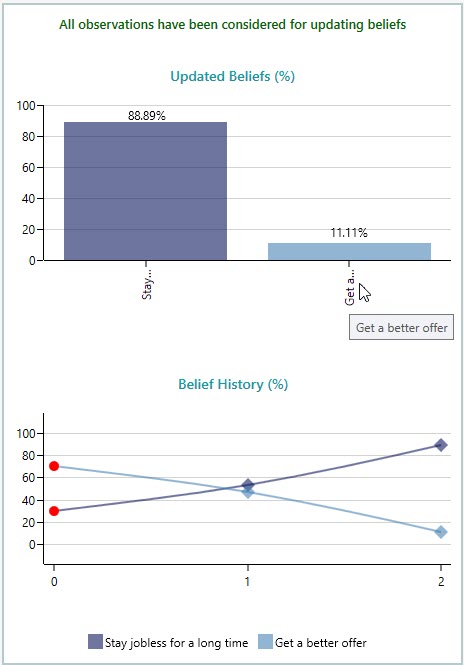
So, you see that your belief of "getting a better offer" changed from 70% to merely 11.11%. Click the Complete button in the Ribbon now.
Once you click the complete button, you will see the Bayesian Inference tool got dismissed and the Decision tree Chance node is updated with the new probabilities. And then, you will see that the decision tree Expected values are updated based on the new probabilities and the policy is now changed from "Wait for a better offer" to the action "Take the job offer at hand".
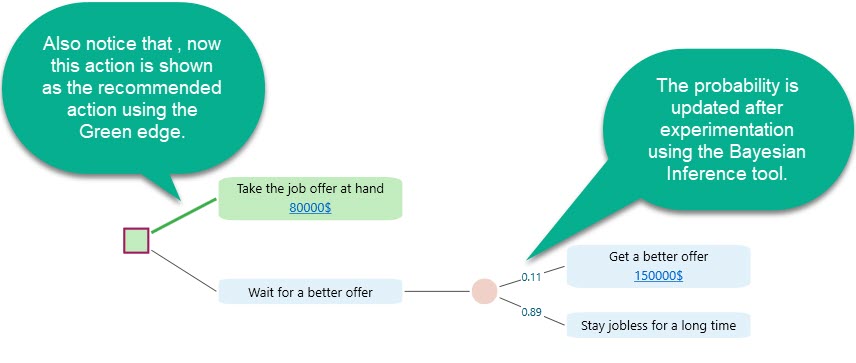
So, we see that Bayesian Inference based experimentation can significantly improve your decision quality. It is always recommended to perform sensitivity analysis and use the Bayesian Inference tool to update beliefs about any uncertainty especially for those events that have probability with high sensitivity.